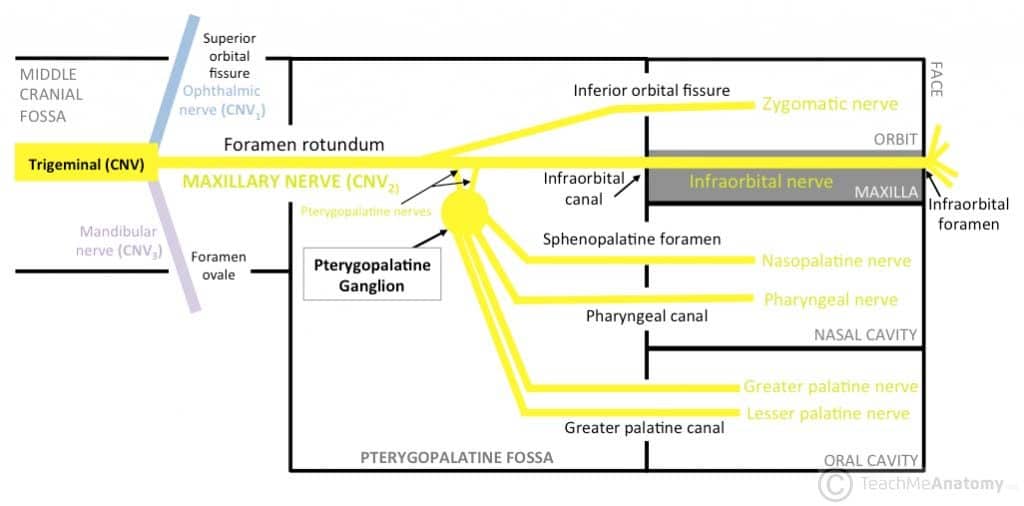
Infraorbital Nerve Orbital Floor
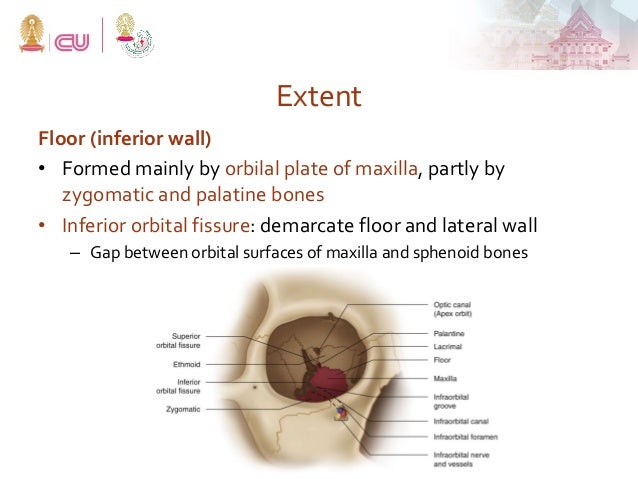
The infraorbital canal is a bony canal within the maxillary bone located at the anterior aspect of the orbital floor.
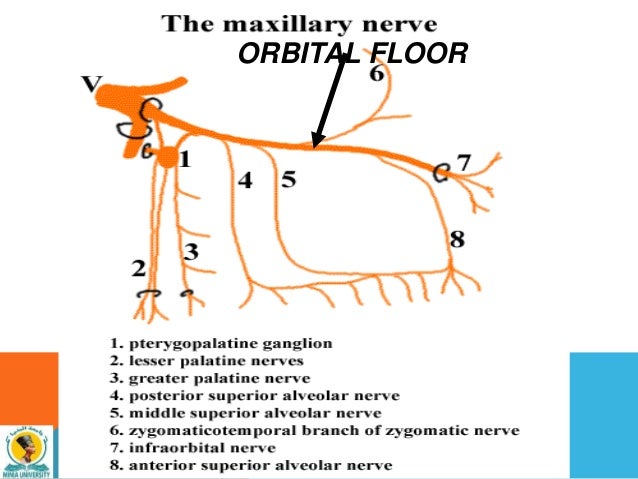
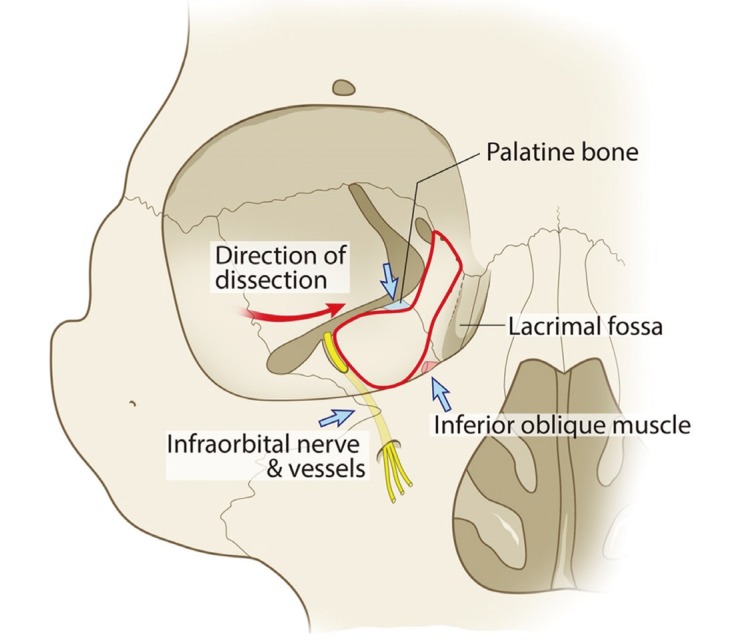
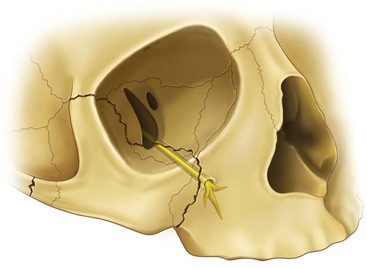
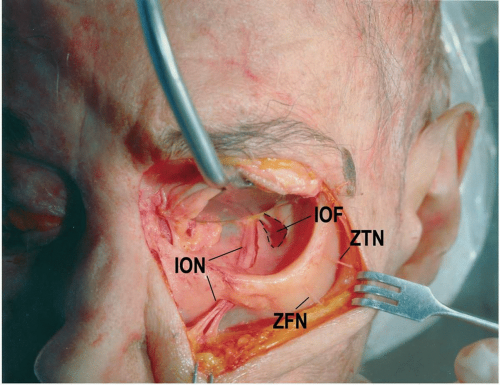
Infraorbital nerve orbital floor. The inferior orbital neurovascular bundle comprising the infraorbital nerve and artery courses within the bony floor of the orbit. Infraorbital nerve transpositioning into orbital floor tioning the infraorbital nerve into the orbital floor before reduction and stabilization of the fractured zygomatic complex. The infraorbital nerve travels with the infraorbital artery and vein. The infraorbital nerve ion a terminal branch of the maxillary nerve travels obliquely from medial to lateral across the orbital floor.
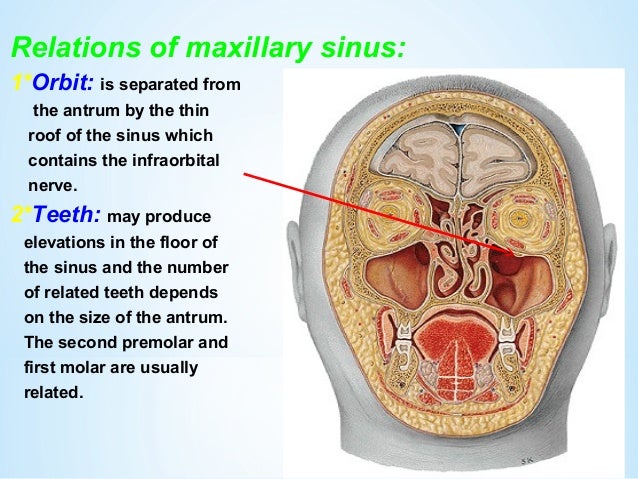
It exits the skull through the infraorbital foramen innervating the lower eyelid lateral nose and part of the superior lip. The inferior orbital neurovascular bundle comprising the infraorbital nerve and artery courses within the bony floor of the orbit. We also look for orbital emphysema. The roof of this infraorbital canal is only 0 23mm thick and the bone of the posterior medial orbital floor averages 0 37 mm thick.
1 this is commonly known as the ion anatomical course. In the anterior portion of the orbit the ion is in a canal and in the middle and posterior portions of the orbit it lies in a groove. The roof of this infraorbital canal is only 0 23mm thick and the bone of the posterior medial orbital floor averages 0 37 mm thick. The canal commences posteriorly as the continuation of the infraorbital groove and terminates anteriorly at the.
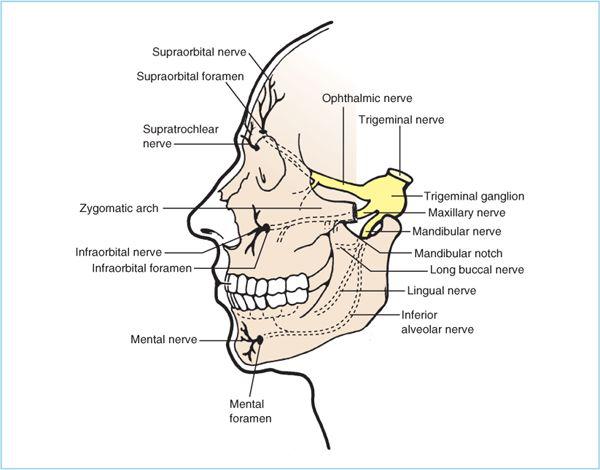
It branches from the maxillary nerve in the pterygopalatine fossa and travels through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It runs anteriorly along the floor of the orbit in the infraorbital groove to the infraorbital canal of the maxilla. Furthermore we verified patients comfort in the postoperative period because of the utmost importance to obtain further parameters useful to validate the applicability of present technique. The anatomy of the orbital floor predisposes it to fracture.
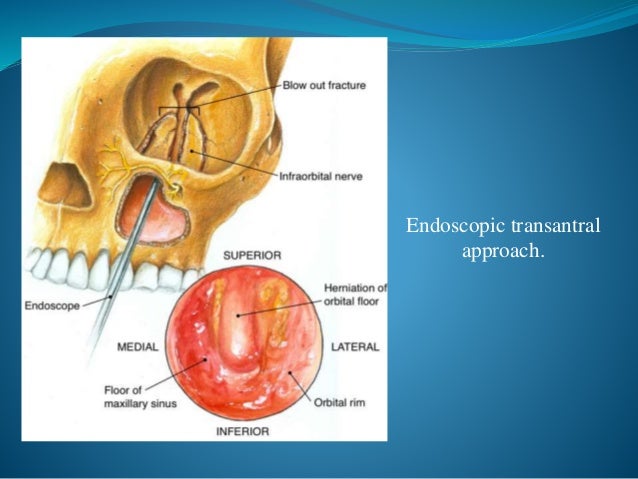
An orbital blowout fracture is a traumatic deformity of the orbital floor or medial wall typically resulting from impact of a blunt object larger than the orbital aperture or eye socket most commonly the inferior orbital wall i e. It transmits the infraorbital nerve which is a branch of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve cn vb as well as the infraorbital artery and vein. If the floor is broken that nerve can be traumatized and you get numbness in the distribution of that nerve. The infraorbital nerve enters the orbit via the infraorbital fissure and passes along the floor of that structure in the infraorbital groove.
The nerve runs in the infraorbital sulcus which crosses the floor of the orbit together with the infraorbital artery and vein. Materials and methods two male and one female patients with history of road traffic accidents reported to the hospital emergency room.















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12543/the-maxillary-nerve_english.jpg)